Copy to clipboard
Copy to clipboard 
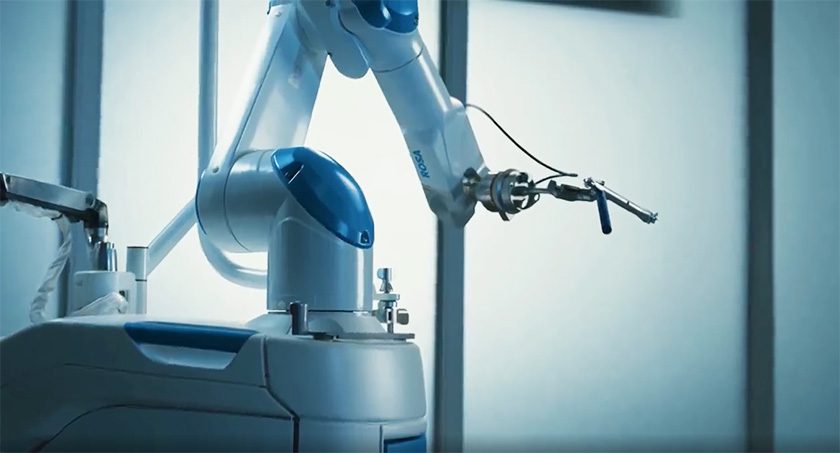
Shoulder joint replacement surgery is an attractive market as growth from the massive knee and hip segments slows down. However, shoulder surgery can be extremely complex. Zimmer Biomet hopes to ease that burden for surgeons with the market’s first robot designed for shoulder joint replacement surgery.
Nnamdi Njoku, Zimmer Biomet’s President, Surgical, Sports, Upper Extremities and Restorative Therapies, answered a few of our questions regarding the company’s upcoming robot and its impact on the market. His answers have been excerpted here for length.
What makes shoulder replacement surgery a good candidate for robotic assistance?
Mr. Njoku: Shoulder surgeries require extreme precision and care, and are strong candidates for robotic assistance given the complexities of many procedures. Glenohumeral joint replacement procedures, for example, are particularly complicated, beginning with challenges in achieving adequate soft-tissue exposure and its inherent constraint on effective visualization of the anatomy. Once exposure is achieved, there continues to be complexity in both the evaluation of the arthritis-induced deformity, as well as the surgical execution of reshaping the glenoid’s orientation in a bone sparing fashion, to the desired pre-diseased state and/or appropriate biomechanical position over a guide-pin.
On the other side of the joint, conventional pre-operative planning tools and instrumentation have had limitations for a surgeon to accurately execute the humeral resection at the appropriate version, inclination and depth measurements. This challenge is, in part, not having the ability to accurately leverage various key bony landmarks, including those in the elbow, which are required inputs to properly prepare the humeral resection.
Due to the complexity of shoulder replacement procedures, malpositioning of the implants can occur. Unfortunately, inaccurate implant placement has been shown to negatively affect clinical and radiologic outcomes in shoulder replacement procedures.1,2
With ROSA Shoulder, surgeons are now equipped with a robotic system that can assist in executing precise, guide-pin-free, and bone-sparing glenoid positioning, along with accurate3 humeral resections along plans that are personalized for patients based on their specific anatomies. They will also have the flexibility to intra-operatively switch from an anatomic total shoulder to a reverse shoulder if required. Robotic solutions, like ROSA Shoulder, will be a critical solution to the future of shoulder orthopedics and will drive innovations that make complex procedures more precise.
How does ROSA Shoulder integrate with the broader ZBEdge ecosystem?
Mr. Njoku: Like all solutions under the ROSA Robotics portfolio, ROSA Shoulder fully integrates with the ZBEdge Dynamic Intelligence ecosystem to deliver cutting-edge, data-driven solutions to unlock the full potential of shoulder procedures. ROSA Shoulder utilizes patient-specific data to help surgeons make informed decisions on shoulder surgeries based on a patient’s specific needs and anatomy, allowing surgeons to accurately complete complex shoulder procedures from reaming the glenoid to completing humeral resections that allow accurate implant placement for the patient.
Further, ROSA Shoulder integrates with Zimmer Biomet’s new Signature ONE Planning System 2.0, which helps surgeons visually plan a procedure pre-operatively. During procedures, ROSA Shoulder provides real-time, intra-operative data to help surgeons execute personalized glenoid and humeral placement procedures, ultimately with the goal of reducing complications for patients.
Being first to market with a novel technology like this can be a double-edged sword. What are some of the opportunities and challenges of trailblazing the shoulder replacement robotics market?
Mr. Njoku: The biggest opportunity Zimmer Biomet stands to benefit is first-mover advantage by providing meaningful technological solutions that solve unmet market needs, which can benefit both surgeons and patients long before other alternatives are commercially available. We are deploying learnings, disciplined tactics, and best practices garnered to scale in a thoughtful manner.
What kind of adoption are you expecting for robotics in shoulder replacement? About the same as large joints?
Mr. Njoku: We look forward to seeing surgeons use ROSA Shoulder across the broad spectrum of shoulder replacement procedures in the short term and long term. At Zimmer Biomet, we have seen the impact robotics have had on making procedures more surgeon-centric, accurate and data-driven, and anticipate ROSA Shoulder will do the same as the first robotic assistant for shoulder arthroplasty on the market.
We see ROSA Shoulder’s potential in optimizing glenohumeral joint replacement procedures and expect the platform to gradually introduce more advanced data analytics to large joint procedures and several other procedures across shoulder orthopedics.
References:
- Gregory TM, Sankey A, Augereau B, Vandenbussche E, Amis A, Emery R, et al. Accuracy of glenoid component placement in total shoulder arthroplasty and its effect on clinical and radiological outcome in a retrospective, longitudinal, monocentric open study. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75791. Epub 2013/10/12.
- Chalmers PN, Boileau P, Romeo AA, Tashjian RZ. Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019 Jun 15;27(12):426-36. Epub 2019/06/07.
- Data on File: FER-JSB231211-01 Rev A
Shoulder joint replacement surgery is an attractive market as growth from the massive knee and hip segments slows down. However, shoulder surgery can be extremely complex. Zimmer Biomet hopes to ease that burden for surgeons with the market’s first robot designed for shoulder joint replacement surgery.
Nnamdi Njoku, Zimmer Biomet’s...
Shoulder joint replacement surgery is an attractive market as growth from the massive knee and hip segments slows down. However, shoulder surgery can be extremely complex. Zimmer Biomet hopes to ease that burden for surgeons with the market’s first robot designed for shoulder joint replacement surgery.
Nnamdi Njoku, Zimmer Biomet’s President, Surgical, Sports, Upper Extremities and Restorative Therapies, answered a few of our questions regarding the company’s upcoming robot and its impact on the market. His answers have been excerpted here for length.
What makes shoulder replacement surgery a good candidate for robotic assistance?
Mr. Njoku: Shoulder surgeries require extreme precision and care, and are strong candidates for robotic assistance given the complexities of many procedures. Glenohumeral joint replacement procedures, for example, are particularly complicated, beginning with challenges in achieving adequate soft-tissue exposure and its inherent constraint on effective visualization of the anatomy. Once exposure is achieved, there continues to be complexity in both the evaluation of the arthritis-induced deformity, as well as the surgical execution of reshaping the glenoid’s orientation in a bone sparing fashion, to the desired pre-diseased state and/or appropriate biomechanical position over a guide-pin.
On the other side of the joint, conventional pre-operative planning tools and instrumentation have had limitations for a surgeon to accurately execute the humeral resection at the appropriate version, inclination and depth measurements. This challenge is, in part, not having the ability to accurately leverage various key bony landmarks, including those in the elbow, which are required inputs to properly prepare the humeral resection.
Due to the complexity of shoulder replacement procedures, malpositioning of the implants can occur. Unfortunately, inaccurate implant placement has been shown to negatively affect clinical and radiologic outcomes in shoulder replacement procedures.1,2
With ROSA Shoulder, surgeons are now equipped with a robotic system that can assist in executing precise, guide-pin-free, and bone-sparing glenoid positioning, along with accurate3 humeral resections along plans that are personalized for patients based on their specific anatomies. They will also have the flexibility to intra-operatively switch from an anatomic total shoulder to a reverse shoulder if required. Robotic solutions, like ROSA Shoulder, will be a critical solution to the future of shoulder orthopedics and will drive innovations that make complex procedures more precise.
How does ROSA Shoulder integrate with the broader ZBEdge ecosystem?
Mr. Njoku: Like all solutions under the ROSA Robotics portfolio, ROSA Shoulder fully integrates with the ZBEdge Dynamic Intelligence ecosystem to deliver cutting-edge, data-driven solutions to unlock the full potential of shoulder procedures. ROSA Shoulder utilizes patient-specific data to help surgeons make informed decisions on shoulder surgeries based on a patient’s specific needs and anatomy, allowing surgeons to accurately complete complex shoulder procedures from reaming the glenoid to completing humeral resections that allow accurate implant placement for the patient.
Further, ROSA Shoulder integrates with Zimmer Biomet’s new Signature ONE Planning System 2.0, which helps surgeons visually plan a procedure pre-operatively. During procedures, ROSA Shoulder provides real-time, intra-operative data to help surgeons execute personalized glenoid and humeral placement procedures, ultimately with the goal of reducing complications for patients.
Being first to market with a novel technology like this can be a double-edged sword. What are some of the opportunities and challenges of trailblazing the shoulder replacement robotics market?
Mr. Njoku: The biggest opportunity Zimmer Biomet stands to benefit is first-mover advantage by providing meaningful technological solutions that solve unmet market needs, which can benefit both surgeons and patients long before other alternatives are commercially available. We are deploying learnings, disciplined tactics, and best practices garnered to scale in a thoughtful manner.
What kind of adoption are you expecting for robotics in shoulder replacement? About the same as large joints?
Mr. Njoku: We look forward to seeing surgeons use ROSA Shoulder across the broad spectrum of shoulder replacement procedures in the short term and long term. At Zimmer Biomet, we have seen the impact robotics have had on making procedures more surgeon-centric, accurate and data-driven, and anticipate ROSA Shoulder will do the same as the first robotic assistant for shoulder arthroplasty on the market.
We see ROSA Shoulder’s potential in optimizing glenohumeral joint replacement procedures and expect the platform to gradually introduce more advanced data analytics to large joint procedures and several other procedures across shoulder orthopedics.
References:
- Gregory TM, Sankey A, Augereau B, Vandenbussche E, Amis A, Emery R, et al. Accuracy of glenoid component placement in total shoulder arthroplasty and its effect on clinical and radiological outcome in a retrospective, longitudinal, monocentric open study. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75791. Epub 2013/10/12.
- Chalmers PN, Boileau P, Romeo AA, Tashjian RZ. Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019 Jun 15;27(12):426-36. Epub 2019/06/07.
- Data on File: FER-JSB231211-01 Rev A

You are out of free articles for this month
Subscribe as a Guest for $0 and unlock a total of 5 articles per month.
You are out of five articles for this month
Subscribe as an Executive Member for access to unlimited articles, THE ORTHOPAEDIC INDUSTRY ANNUAL REPORT and more.
ME
Mike Evers is a Senior Market Analyst and writer with over 15 years of experience in the medical industry, spanning cardiac rhythm management, ER coding and billing, and orthopedics. He joined ORTHOWORLD in 2018, where he provides market analysis and editorial coverage.